
Content
- Cutting grapevines - tutorial with instructions
- Worth knowing about growth
- Cutting types and dates
- Cut on the day of planting
- foray
- Cordon - beginner-compatible espalier form
- Educate wine grapes clearly
- Winter cut - step-by-step instructions
- background
- Observe the correct cutting technique
- Summer cut ensures order
- Water guns and Geiztriebe break out
- Rejuvenate old grapevine
- frequently asked Questions
- Are grapevines self-fertile?
- I have acquired a grape vine with three shoots, which I would like to raise up to the balcony with a single trunk. How do I best go about cutting the picture?
- If I plant vines for wall greening in the tub, how big should the jar be?
- Our house facade is planted with beautiful grapevines and should now be renovated. How can the vines survive this?
- We would like to educate our new grapevine in fan shape. What should be paid particular attention?
- We would like to plant our 80 cm wide pergola with grapevines. How does it work?
- Should I cut my grapevines in the fall or spring?
- My grape "Lakemont" has grown nicely and already bears small grapes on its two shoots. I would like to raise the vine horizontally on our house wall. How does that succeed?
- The 3 most common cut defects
- Tips

From the age of 4 years, the vine is no longer raised but kept fruitful with conservation or rejuvenation cuts
Cutting grapevines - tutorial with instructions
Grape vines should be cut twice a year. Why this is so and how to do it right explains this tutorial. After reading these editing instructions, magnificent, high-yielding vines are no longer a pious wish for hobbyists.
Worth knowing about growth
For an introduction to the perfect cut care of grapevines we invite you to a short excursion into the botanical basics. The type and extent of the cut can be better estimated if you are familiar with the following aspects:
It requires a framework structure of old, at least two years old wood, so that fruit rods can grow. In the winter, the gardener chooses medium-strength shoots (6-10 mm in diameter) from the one-year-old wood, which are located at intervals of 10 to 20 centimeters on the lateral framework legs. At its base are the budding plants of the previous summer, which are blooming and fruiting this year.
Cutting types and dates
As a lonely shoot or small tuft of tufts grapevines find their way into the hobby garden. In order for beautiful, high-yielding vines to develop, cut care plays a key role. First contact with the pruning shears have the berry bushes on the day of planting. This is followed by a three-year education, which leads to a continuous maintenance phase. Recommended cuts for decorative and productive growth summarizes the following overview:
Cut on the day of planting
The best time for vines to grow is from mid-May to mid-April. Before the young berry bushes are for sale, you have gone through a phase of refining. By expert hand, a scion is grafted onto a sturdy base. When planting it is essential to ensure that the thickened finishing point is at least 10 centimeters above the ground. In the last step of planting a vine gets its first cut. How to do it right:
All vines are happy about a plant disk of 50 to 100 centimeters in diameter. At least a plate-sized recess around the root plate should be permeable to water. A mulch layer of foliage, dried grass clippings or bark mulch is very welcome to a freshly planted grapevine.
foray
Cordon - beginner-compatible espalier form
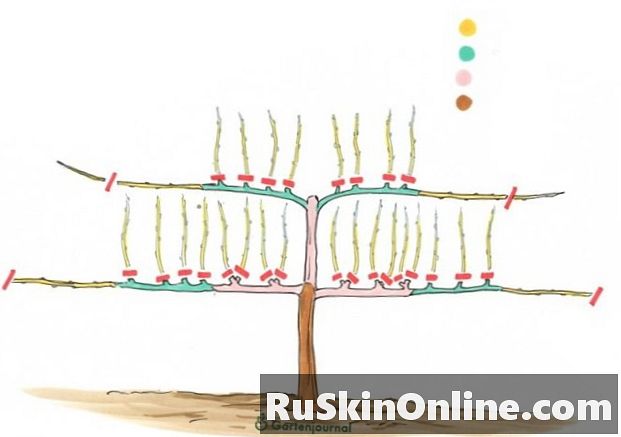
Kordon is the progenitor of all climbing forms for climbing plants. Beginners in the cultivation of grapevines like to use the uncomplicated education variant back. A cordon is made up of a short trunk, whose thighs educate you horizontally on both sides. Rope aids are rope systems, grid constructions or simple wires that you place between two posts in order to tie the wine rods to them. In order to green a meter-high facade, a cordon is piled up floor by floor. The ideal distance between two floors is 60 centimeters.Educate wine grapes clearly
In the first year, vines are to develop a long, strong and well woody stem. More shoots from the refining station break off. Tie the main shoot continuously so it is growing straight. At the end of the summer, the future trunk is roughly pencil-thick and two to three meters long. If the chosen form of education does not require a long trunk, cut the shoot back to 100 to 150 centimeters in August. If a long trunk is desired, summer pruning is eliminated. In February of the following year begins the sectional drawing to Kordon, which extends under normal conditions for three to four years. How to proceed:
If your vines come from a competent nursery school, the first fruit wood is formed during the education. Side shoots grow out of the buds of the horizontal scaffolding branches. These cut back on two buds the following winter so that they flower and fruit for the first time. Parallel to the cutting work, you regularly tie up scaffolding branches and side branches to the trellis.
Educate grapevines as cordon with short stem and side thighs. The scaffolding drives extend in all directions annually by 100 centimeters. The horizontal side rods carry the precious fruit wood.These shoots cut vigorously back in the winter on two buds during the educational phase in winter.
Winter cut - step-by-step instructions
The education is completed at the beginning of the fourth year. In February, the starting signal is given for the annual, winter main section. This primarily aims at the preservation of young, productive fruited rods. How to cut your grapevines in winter:
As illustrated below, in the winter cut, give priority to those shoots that are the main shoot or trunk stand closest, Proximity to the scaffold is more important than the direction of growth. It is of secondary importance whether the recut fruit branch points to the left, right or up. All other rods that leave a knot cut at the base, without stubs.
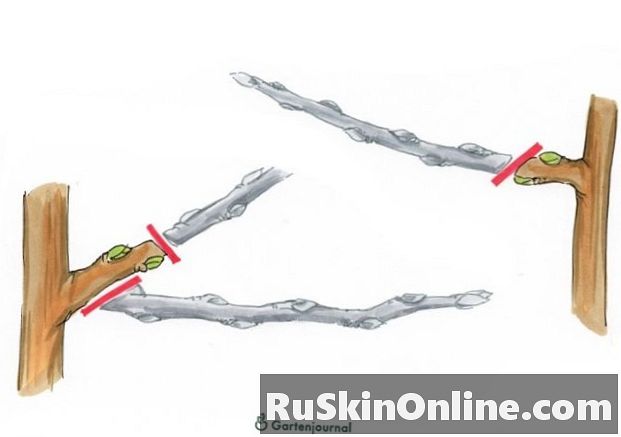
In February, cut all the removed rods back to two eyes. If several shoots have formed, remove the or the outer fruit shoots. Only the shoot that is closest to the scaffold, shorten to two eyes, so that this year he flowers and fruit.
background
Observe the correct cutting technique
The key to success in pruning is the expert editing technique. If you bring up horizontal scaffold shoots or complete the winter fruit woodcut, the buds are in focus. Put the pruning shears in close proximity to an eye. Please do not cut into a bud and do not leave a long stub. A light one Sloping of the scissors ensures that the sap leaves in the desired direction and does not drown deeper buds.
Summer cut ensures order
In the summer the new fruit branches grow from the buds of lateral tendrils. In parallel with the progress of growth, tie these shoots vertically to the frame. Under normal conditions, 10 to 15 leaves have developed on each tied rod by mid-summer. So much leaf mass is not needed to supply the grapes. Furthermore, the increasingly long, densely leafed tendrils cast shadows on the fruits. In the summer hobby winemakers therefore resort to the pruning shears again and ensure order. How to do it right:
From the buds below the interfaces then drive off fresh tendrils. The younger the vine, the more vigorous the re-budding. So that shoots and leaves do not consume valuable plant energy, they should be removed regularly. If you stay on the heels continuously, you can easily break them off in the herbaceous state. It is important to note that above the last grape a sufficient number of at least four leaves remain.
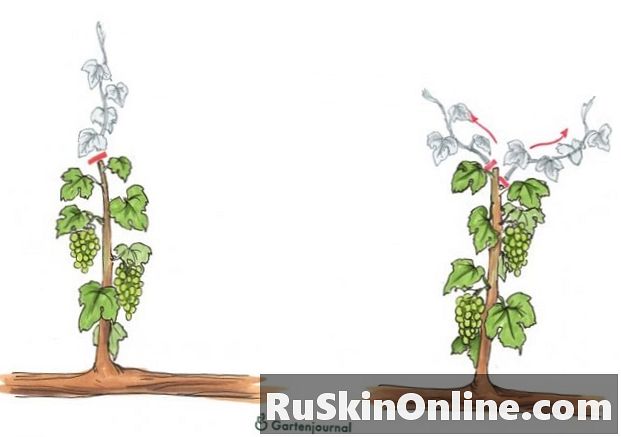

In summer, cut fruit shoots back to about four leaves above the last grape (1). After the cut new tendrils drift out, which cut you away or break out in a timely manner (2).
Water guns and Geiztriebe break out
You do not need a pair of scissors for a continuous action during cutting care. Popular varieties tend to float numerous water drops from sleeping eyes in the old wood throughout the season. In addition, shoots of leaf axles sprout, as they are known from the cultivation of tomatoes. From these branches are no flowers or grapes to be hoped for. On the contrary, the unwanted Triebaren deprive the vine of important reserves and want to overgrow fruitful rods to get to light. To prevent this, you put a stop to the following strategy:
Check your vines regularly from spring on water shoots and Geiztriebe. With a length of 10 to 30 centimeters, the barren branches are easiest to remove. If a water shot has escaped your attention and is already woody, cut it off at the base.
Rejuvenate old grapevine
A vine as a floral ensemble can be several hundred years old. However, this does not apply to individual scaffold drives or legs. Departures on the truss tend to become more and more gnarled after years. Dense adhesions prevent the budding of fresh shoots. At this point brings one local rejuvenation new momentum for growth. How to exchange an older scaffold drive successfully:
A rejuvenation cut, as it is commonplace in other bushes, can not tolerate grapevines. Characteristic of vines is that the trees hardly form wood wounds to overflow cut surfaces. The massive juice flow also contributes to the fact that large cuts do not close or hesitate and wound closure agents do not adhere. To put an old grapevine completely on the stick usually ends in total failure.
frequently asked Questions
Are grapevines self-fertile?
Grapevines are usually self-fertile. One single plant is enough to harvest juicy grapes. The yield increases noticeably when you combine two or more grape varieties.
I have acquired a grape vine with three shoots, which I would like to raise up to the balcony with a single trunk. How do I best go about cutting the picture?
Select the strongest shoot and tie it to a support bar. The other two shoots cut back on the floor. If the remaining shoot reaches the planned height, let it grow another 50 centimeters. Then cut the trunk in half. Briefly put the scissors over one eye. From this point, the grapevine will branch out and can be trained according to plan.
If I plant vines for wall greening in the tub, how big should the jar be?
A bucket should always match the size of the plant. Therefore, weigh in advance how far a vine may spread. The orders of magnitude for suitable buckets thus range from 20 to 50 liters. If you are planning the greening of a pergola or a majestic facade, it may be a bit more volume. It is important that the root can develop unhindered to supply the leaf mass.
Our house facade is planted with beautiful grapevines and should now be renovated. How can the vines survive this?
Best option for solving the problem is moving the vines. Thoroughly clear the vines to reduce plant mass. Then loosen the tendrils from the jungle gym to lay them on the ground. It's amazing how flexible even thick trunks are and can be easily folded. Ideally, a temporary trellis will be available until the completion of the renovation or you will simply fix the tendrils to the scaffolding.
We would like to educate our new grapevine in fan shape. What should be paid particular attention?
In contrast to the one to two-armed cordon, the fan shape usually has five legs. Initially raise the trunk to a height of 50 to 60 centimeters plus five buds. Above the fifth bud, cut the main stem. This results in a juice jam, which opens in the shoot of five side branches. Remove further shoots from the refining office as competition to the tribe as well as excess side shoots. To create an airy, shapely fan, fix the individual legs on the trellis at a distance of 50 to 60 centimeters.
We would like to plant our 80 cm wide pergola with grapevines. How does it work?
Initially lead the trunk of the vines in the air. At the top, bring the scaffold parallel to the spar and tie the tendrils regularly. Every 10 to 15 centimeters leave a side shoot. These side shoots cut in every winter on 2 eyes. A stable construction succeeds if every year for the horizontal trunk extension between 3 and 6 new side shoots are added.
Should I cut my grapevines in the fall or spring?
Vines are early in the juice and can severely "bleed" from cuts. It is therefore advisable to perform the cutting of grapes during the saffron. The best time for the main cut is immediately after the main frost period in February. You can cut vines in the fall though. However, there is a risk that the tendrils will dry in the winter or freeze completely.
My grape "Lakemont" has grown nicely and already bears small grapes on its two shoots. I would like to raise the vine horizontally on our house wall. How does that succeed?
The good-natured cut tolerance of grapevines allows for a variety of educational options, including the horizontal facade greening counts. When you cut off a vine, new side shoots drift below the interface in the range of 10 to 20 centimeters. These bind you to the trellis according to your own ideas. The only premise is a sufficient distance of about 50 centimeters. At the end of February you will cut the side shoots on 2 buds. At the end of June, cut fruit rods down to five leaves above the last grape. On this occasion you remove disturbing and unfruitful branches. In August, look for leaves that shade a grape to remove it.
The 3 most common cut defects
The frustration is great when grapevines turn into an impenetrable scrub. From the longed for grapes is far and away no trace. Just as devastating for the hobby winemaker, when an ancient grapevine comes in after the rejuvenation cut. To keep the readers of this tutorial from such disappointments, the following table lists the three most common editing mistakes with tips for successful prevention:
YoutubeTips
Every grapevine root is unique. If a vine is exhausted after many years, do not throw away its roots. With a little imagination, use the bizarre rhizomes for a sensational decoration. Simply attach a piece of floral foam on it and decorate it with seasonal flowers - the unique piece is complete.